About APRA’s Prudential Handbook
The Prudential Handbook allows you to search and browse APRA’s prudential standards currently in force. It also allows you to search and browse prudential practice guides and other information related to the standards. The Prudential Handbook does not replace the Federal Register of Legislation, which contains the authorised versions of all prudential standards (and other legislative instruments made by APRA).
The Prudential Handbook uses the same structure as the prudential framework. Use it to access all prudential standards and guidance relevant to your industry.
We are interested in your feedback. Please email feedback on the Prudential Handbook to:
PrudentialHandbook@apra.gov.au
APRA's prudential framework
APRA sets legal requirements and guidance for the entities it regulates (the prudential framework).
The prudential framework comprises:
- legally binding prudential standards
- legally binding reporting standards
- supporting guidance (such as prudential practice guides).
Each industry that APRA regulates – that is, banking, insurance, and superannuation – has specific prudential standards, prudential guidance and reporting standards that apply to them. In addition, APRA has standards and guidance that apply to multiple industries; these are known as cross-industry standards and guidance.
How the framework is structured
The framework is organised into pillars (or categories). Each pillar focuses on one aspect of an entity’s legal responsibilities, including the risks they must manage. There are four pillars that apply to all entities: Governance, Risk Management, Recovery and Resolution, and Reporting. The fifth pillar depends on the industry: for banking and insurance, it is Financial Resilience; for superannuation, it is Business Operations. Sub-pillars within each pillar further group similar standards and guidance together.
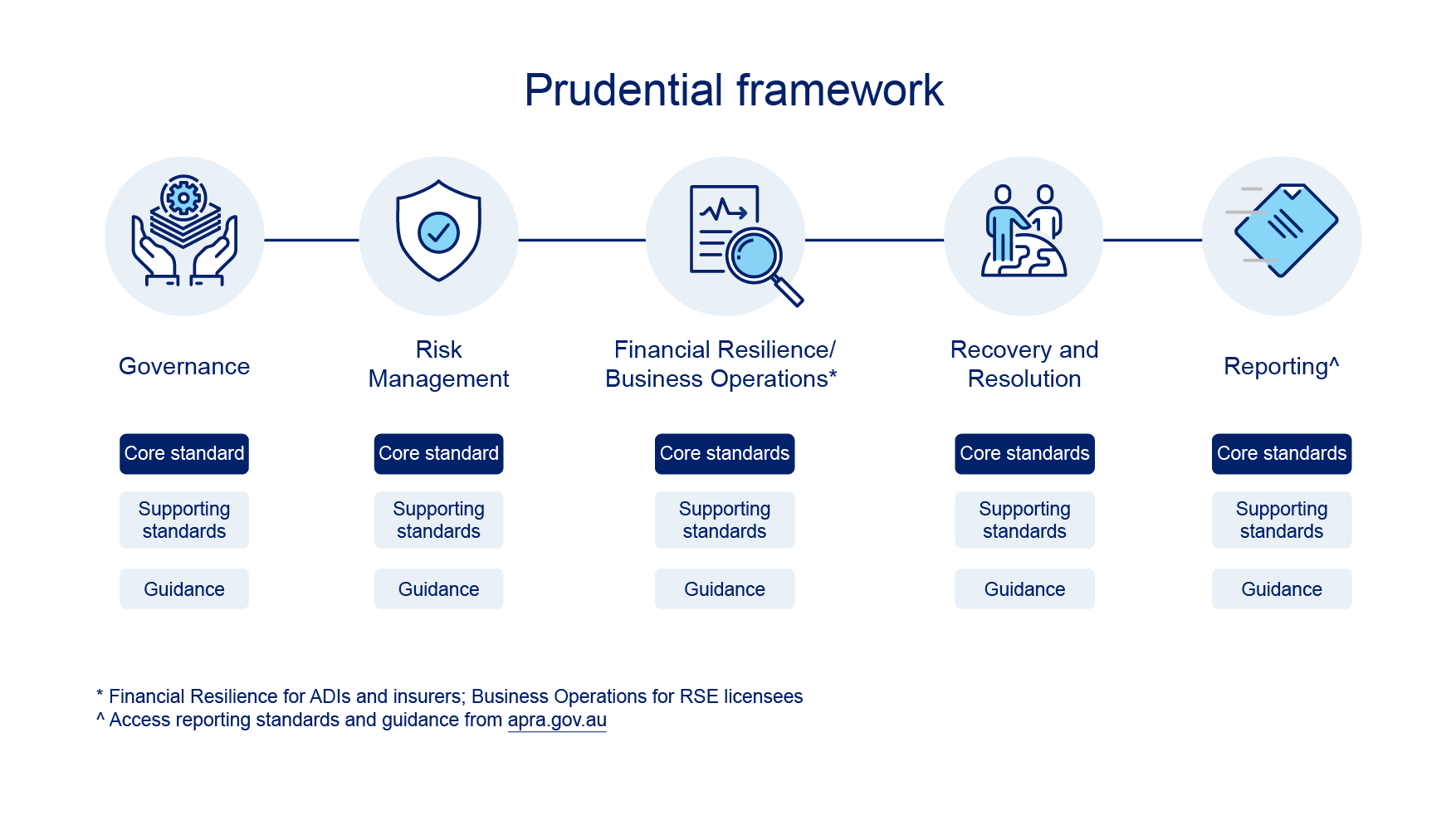
Within each pillar are core standards, supporting standards and guidance. Core standards set foundational requirements. Supporting standards are narrower in focus, providing extra detail about particular risks or industries. Guidance typically means prudential practice guides (PPGs). Other forms of guidance include letters, FAQs, and information papers. These provide APRA’s view of sound practice in particular areas.
The pillars
Governance standards require entities to act with honesty and integrity, and to be run by people with the right skills, knowledge and experience. The Governance Pillar includes requirements for good governance, and the fitness and propriety of people in positions of responsibility. It applies to all industries.
Risk Management standards require entities to maintain effective risk management strategies and systems. The Risk Management Pillar includes requirements about managing operational risk, and risks specific to an industry including credit risk, insurance risk and investment risk. It applies to all industries.
Financial Resilience standards require entities to maintain adequate financial resources to withstand stresses. The Financial Resilience Pillar includes requirements such as maintaining capital and liquidity. It applies to the banking, general insurance, life insurance and private health insurance industries.
Business Operations standards require RSE licensees to manage their business operations to achieve the outcomes they seek for members. They include requirements for strategic planning, investment governance, operational risk resourcing and insurance. It only applies to the superannuation industry.
Recovery and Resolution standards require entities to strengthen crisis preparedness. The Recovery and Resolution Pillar includes requirements such as resolution, recovery and exit planning. It applies to all industries.
Reporting standards apply to all industries. These standards are not currently included in the Prudential Handbook. Access reporting standards from the APRA website.